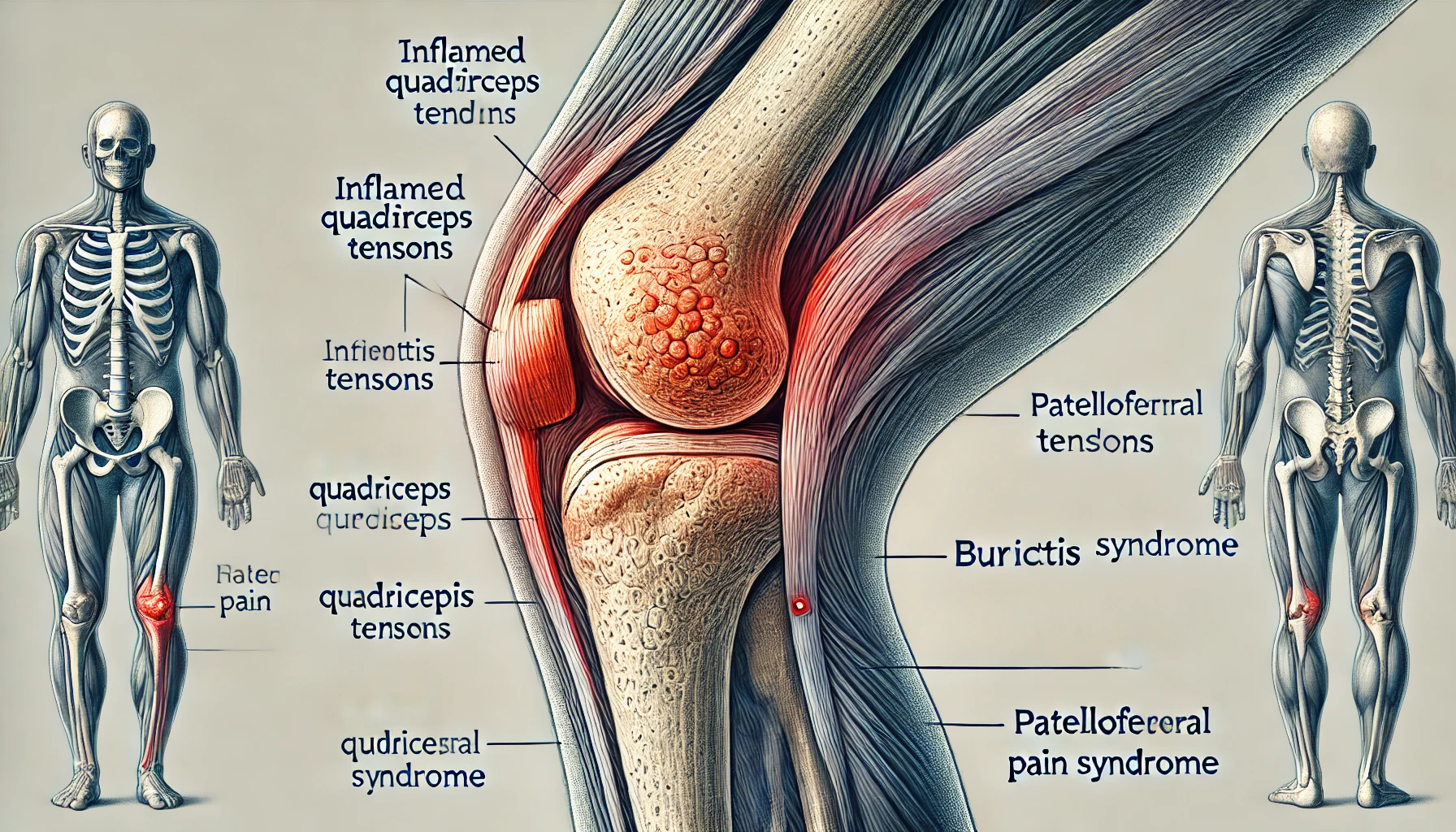
If you’re experiencing tenderness above the kneecap, you’re not alone. Many people, from athletes to office workers, deal with this discomfort, which can interfere with daily activities like walking, climbing stairs, or even sitting for extended periods.
In this article, I’ll explain the common causes of tenderness above the knee cap, effective treatment options, and how to prevent it from happening in the future.
Common Causes of Tenderness Above the Kneecap

Tenderness in this area is usually caused by inflammation, overuse, or injury. Here are the most common reasons:
1. Quadriceps Tendonitis
This condition occurs when the quadriceps tendon, which connects the thigh muscles to the kneecap, becomes inflamed due to repetitive stress or sudden injury.
Symptoms:
✔️ Pain and tenderness above the kneecap
✔️ Swelling and stiffness in the knee
✔️ Discomfort when straightening the leg
Causes:
- Overuse from running, jumping, or squatting
- Weak or tight thigh muscles
- Sudden increase in activity level
2. Suprapatellar Bursitis
The suprapatellar bursa is a fluid-filled sac above the kneecap that reduces friction between the bone and soft tissues. When it gets inflamed, it can cause pain and tenderness above the knee cap.
Symptoms:
✔️ Swelling and warmth above the kneecap
✔️ Pain when bending or extending the knee
✔️ Tenderness to touch
Causes:
- Frequent kneeling (common in athletes and laborers)
- Direct trauma to the knee
- Bacterial infection (in rare cases)
3. Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (Runner’s Knee)
This condition occurs when the kneecap doesn’t move properly within the femoral groove, causing pain in and around the knee.
Symptoms:
✔️ Dull, aching pain above and around the kneecap
✔️ Pain worsens with activities like running, climbing stairs, or prolonged sitting
✔️ Grinding or popping sensation in the knee
Causes:
- Poor knee alignment
- Weak thigh or hip muscles
- Overuse from repetitive movements
4. Arthritis (Osteoarthritis or Rheumatoid Arthritis)
Arthritis is a common cause of chronic knee pain and tenderness. It leads to cartilage breakdown, which results in joint stiffness and discomfort.
Symptoms:
✔️ Gradual onset of pain and stiffness
✔️ Swelling and tenderness around the knee
✔️ Pain worsens with movement and improves with rest
Causes:
- Aging and wear-and-tear of the knee joint
- Autoimmune conditions (in rheumatoid arthritis)
- Previous knee injuries
5. Muscle Strain or Imbalance
Tight or weak quadriceps muscles can put extra strain on the knee joint, leading to tenderness and discomfort above the kneecap.
Symptoms:
✔️ Soreness and tightness in the front of the thigh
✔️ Pain after prolonged standing or sitting
✔️ Feeling of weakness or instability in the knee
Causes:
- Lack of proper stretching or warm-ups
- Muscle fatigue from excessive exercise
- Poor posture or biomechanics
How to Treat Tenderness Above the Kneecap
1. Rest and Activity Modification
If your knee pain is due to overuse or strain, rest the joint and avoid activities that worsen the pain, like running or squatting.
2. Ice and Heat Therapy
- Ice packs (15-20 minutes every few hours) help reduce swelling and numb pain.
- Heat therapy (like warm compresses) relaxes tight muscles and improves blood circulation.
3. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening and stretching the muscles around your knee can prevent further irritation. Try these exercises:
✔️ Quadriceps Stretch – Improves flexibility in the front thigh muscles.
✔️ Straight Leg Raises – Strengthens the quadriceps without putting pressure on the knee.
✔️ Hamstring Stretch – Reduces tightness in the back of the thigh.
✔️ Wall Sits – Builds endurance in the thigh muscles for better knee support.
4. Knee Braces and Compression Sleeves
Wearing a knee brace or compression sleeve can provide support, reduce inflammation, and ease pain.
5. Pain Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen (Advil) or acetaminophen (Tylenol) can help manage discomfort and inflammation.
6. Physical Therapy
A physical therapist can create a customized exercise program to strengthen your knee, improve flexibility, and correct movement patterns that contribute to pain.
Also Read: Pain Above Knee – Causes, Treatment, and Prevention!
How to Prevent Tenderness Above the Kneecap
1. Strengthen Your Leg Muscles
Strong quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes help support the knee and reduce strain on the joint.
2. Warm Up Before Exercise
Always stretch and warm up before physical activity to prevent muscle strain and tendon injuries.
3. Use Proper Footwear
Wearing supportive shoes with good arch support can reduce stress on the knee and improve alignment.
4. Avoid Overuse and High-Impact Activities
If you experience knee tenderness, reduce activities that put excessive stress on your knees, like jumping, deep squats, or running on hard surfaces.
5. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Extra weight increases pressure on the knee joint, so losing even a few pounds can reduce knee pain and tenderness.
When to See a Doctor
If your tenderness above the kneecap:
❌ Lasts more than two weeks despite home treatment
❌ Is accompanied by swelling, redness, or warmth
❌ Causes difficulty walking or bearing weight
❌ Occurred suddenly after an injury
…it’s best to seek medical advice to prevent long-term damage.
FAQ’s
1. Why do I feel tenderness above my kneecap?
Tenderness above the kneecap is often caused by quadriceps tendonitis, suprapatellar bursitis, patellofemoral pain syndrome, or muscle strain. Overuse, repetitive movements, or inflammation in the knee joint can lead to discomfort in this area.
2. How can I tell if my knee pain is serious?
If your knee pain is severe, persistent for more than two weeks, or accompanied by swelling, redness, or difficulty moving, it may indicate a serious condition like arthritis, infection, or ligament damage. In such cases, seeing a doctor is recommended.
3. Can I treat tenderness above the kneecap at home?
Yes! Most cases can be managed with R.I.C.E. (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation), gentle stretching, strengthening exercises, knee braces, and over-the-counter pain relievers. However, if the pain worsens or doesn’t improve, consult a healthcare provider.
4. What exercises should I avoid if I have knee tenderness?
Avoid high-impact exercises like running, deep squats, jumping, or lunges if they cause pain. Instead, opt for low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, or light stretching to prevent further irritation.
5. Can poor posture or weak muscles cause tenderness above the kneecap?
Yes! Weak quadriceps, hamstrings, and hip muscles can put extra strain on the knee joint, leading to pain and tenderness. Poor posture and improper movement patterns can also contribute to knee discomfort. Strengthening these muscles can help prevent issues.
6. When should I see a doctor for knee tenderness?
You should see a doctor if your tenderness above the kneecap:
❌ Persists for more than two weeks despite home care
❌ Causes difficulty walking or bearing weight
❌ Is accompanied by swelling, warmth, or redness
❌ Develops suddenly after an injury
If any of these apply, seeking medical advice can help diagnose the issue and prevent further complications.
Final Thoughts
Tenderness above the kneecap can be uncomfortable and frustrating, but in most cases, it can be managed with rest, ice, gentle exercises, and proper knee care. Identifying the underlying cause of your pain is key to finding the right treatment and preventing further issues. If your symptoms persist or worsen, don’t ignore them—seeking medical advice early can help prevent complications and get you back to pain-free movement faster.
Related Post
- Zimatejigemo – Unlocking the Fusion of Creativity, Identity, and Innovation!
- Tinaypimatelate – The Revolutionary Concept Shaping the Future of Innovation!
- Limhuloxidpov – A Complete Guide to Understanding This Unique Concept!
- Zaxtexporoz – Exploring the Emerging Concept of Innovation and Digital Transformation!
- Lekulent – The Breakthrough Wellness Solution Taking the Health World by Storm!